【ProAV Lab】What's Needed for Successful Streaming at Your University?
Lumens Editor Group
January 02, 2020 29847

Introduction
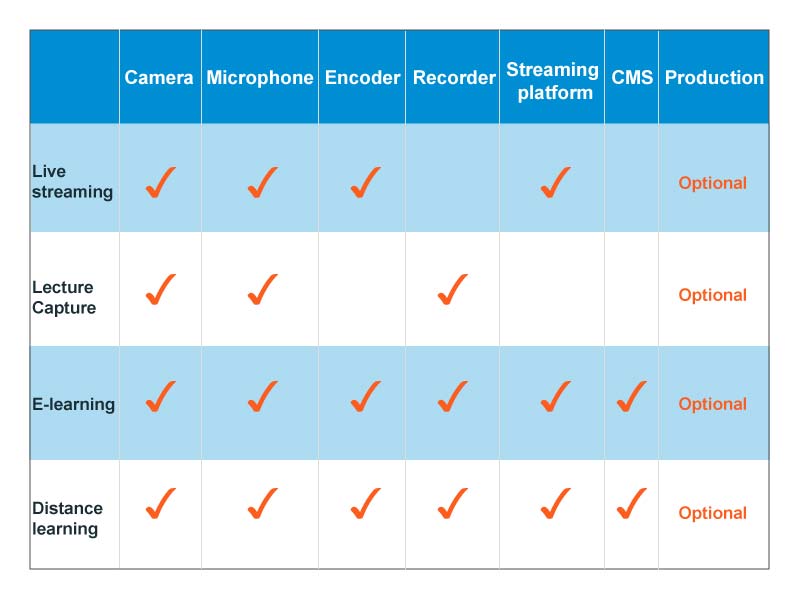
Live streaming is turning the traditional lecture room inside out. Most of the major universities are now using streaming solutions for delivering content to students and the community, and smaller schools are finding it useful for “virtually” increasing the size of their classrooms. Streaming technology can take several forms:
• Live streaming of lectures, seminars, sports, and campus events
• Lecture capture to make classroom content available anytime.
• Online learning or e-learning
• Distance education
How can your university get started with streaming? Understanding all the factors can be overwhelming. Depending on your streaming goals, you will need different tools. Our Streaming Toolkit has four elements:
• Video and audio capture
• Production tools
• Encoding for streaming
• Recording and content management
Cameras and microphones will ensure that your content can be seen and heard by viewers. If you’re streaming a live class, microphones should be used not only for the lecturer, but throughout the classroom as well so student questions can be incorporated into the content. PTZ cameras are highly useful for tracking lecturers as they move around the room, and wireless lavaliere microphones also permit freedom of movement. If lecturers use a podium, box cameras and stand-mounted microphones are suitable.
You will also need to stream the instructor’s visual content; see Production Tools below.
You will also need to stream the instructor’s visual content; see Production Tools below.
.jpg)
2. Production Tools
- It’s important to keep the content both highly visible and interesting. A camera that is focused strictly on a lecturer for the entire class won’t create student engagement. Multiple shots including stage view, lecturer view, and students' view can be incorporated into layouts, which will help you merge different looks into one stream via simple switching functions. You also can create a title/logo overlaying on the stream.
- Powerpoint presentations, Smartboard content and outputs of document cameras will also be a part of your overall production. Wireless presentation systems make it easy for the lecturer to share content from their computer to both the video screens in the classroom and the encoder; split screen capabilities allow multiple types of content to be seen simultaneously.
3. Encoding for streaming
- Encoders are used to prepare audio and video content for streaming. Your video feed will likely include multiple cameras as well as content/document sharing, so ensure that your encoder has an adequate number of inputs. From here, your content goes to an Internet connection.
- Streaming can take several forms: it can be sent live via WiFi around campus; it may be accessed via the university’s website; it can be sent to a YouTube channel, etc. Offsite hosting services can provide analytics as well as live streaming. If you plan to use an offsite service, search for “Online Video Platforms”.
4. Recording and content management
- An alternative to live streaming is recorded content, which allows students to stream classes at their convenience and permits “anytime” viewing of lectures and special events. Many encoders offer recording functions, or you can use a separate recording device.
- Video content management systems (CMS) are used to manage your streaming content and make it accessible to students. Several CMSs, such as Panopto, Kaltura, and Opencast allow instructors to add interactive features and create customized pathways for different students.
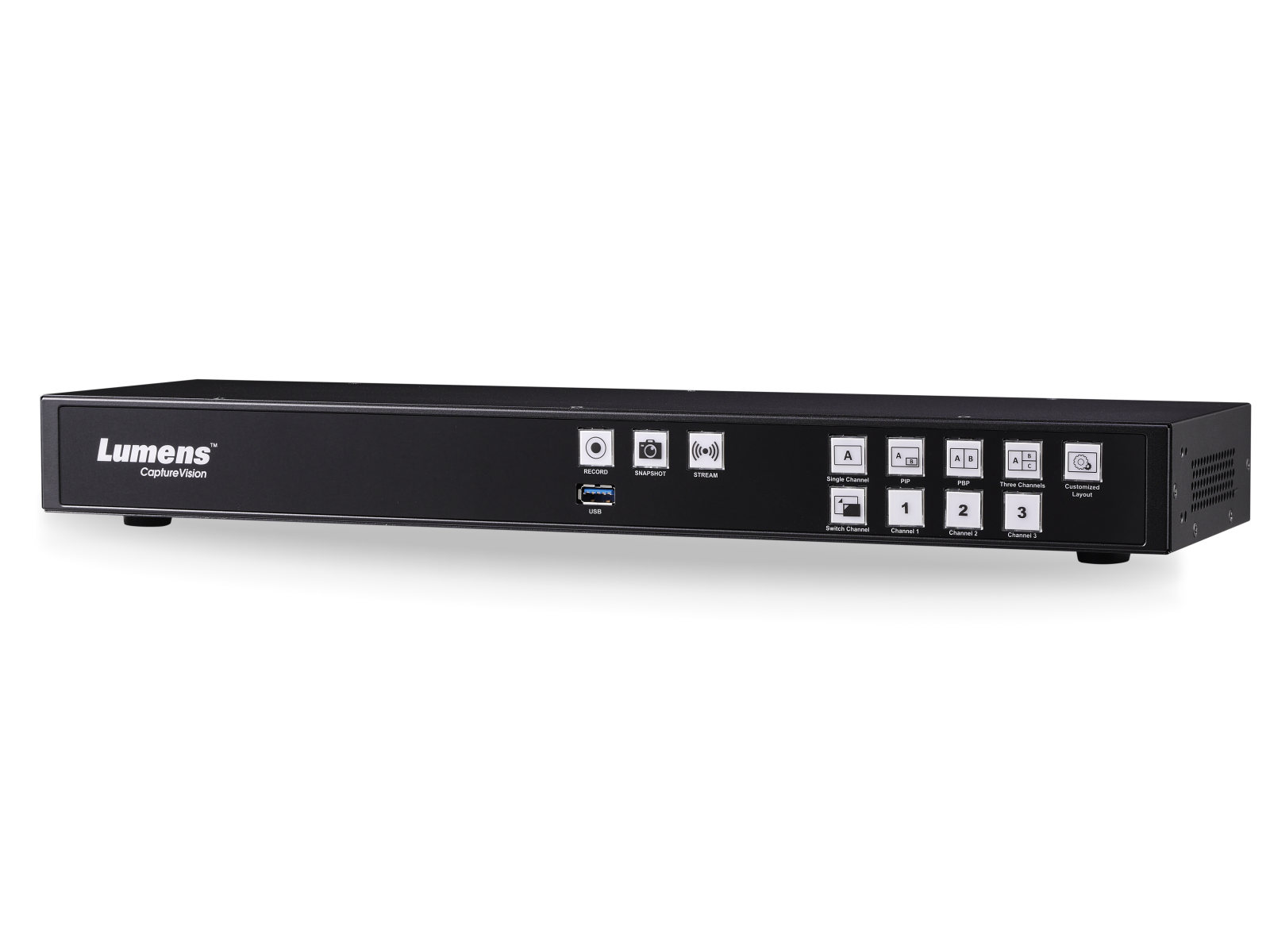

Hardware media processor – the easy way to make it happen
Generally, a hardware media processor not only has encoding, recording, and primary production functions but also integrates with the majority of live streaming platforms and CMSs. Compared to software, a hardware encoder setup involves fewer variables and is less complicated. It is possible to create a quick and repeatable process. For schools and organizations that use live streaming regularly, a hardware media processor provides a smoother, more consistent, and high-quality streaming operation.
With the proper tools, live streaming for education will change the future of teaching and learning in universities.